In the world of trading, hedging is always considered a balancing act. In forex trading, a hedge can be simply defined as a type of transaction that is executed to protect an anticipated or existing position from an unanticipated move in exchange rates. Investors, traders and business all use forex hedges. To hedge, a forex trader has to hold a long and short position in the same FX pair, simultaneously. While the market figures out which direction to go, hedging can be a great way for traders to reduce their risk. Once the market changes and starts trending, traders can start to earn profits from their winning trades while minimizing losses from their losing ones.
So how to go about hedging?
To hedge, you should strategically place trades so that the gain or loss in one position is offset by the gain or loss in another. You can achieve this through a myriad of strategies. For instance, you can choose to trade currencies that tend to move in a different direction than the other ones in your portfolio. In other words, we can say that loss to initial position + gain to hedge = Reduced risk or Neutral exposure.
You should only hedge when it's justified by the reduced risk, as there are expenses associated with opening a new position. Your hedge will recover some or all losses if the original position declines in value. Alternatively, in case the original position remains profitable, you will still be able to cover the cost of the hedge plus generate a handsome profit.
The amount of capital you are investing is a crucial factor in hedging. Thus you should create a budget to ensure that you do not exhaust your funds. On the question of how much money one should hedge, the answer depends on the nature of each trader, particularly, their available capital and their risk attitude.
The main aim of hedging is to protect a longer-term investment from a temporary decline in trade. This limits losses to a specific amount. It’s a good alternative to a stop- loss if the trader has positive sentiments about the market in the long run. This differs from a stop- loss where it eliminates the potential for future profit when automatically closing trades.
Hedging Strategies for Novice Traders
There a myriad of methods that you can use to hedge. However, some of them are complicated and are fit for more experienced traders with a larger skill set. Nevertheless, some strategies are simple enough that they can be used by novice traders. Some of these strategies have been explained in brief below.
Trading safe havens
Certain financial instruments and currencies that tend to retain their value or increase their price during periods of an economic downturn are categorised as safe-haven assets. When trading forex, gold can be used as both a safe-haven as well as a hedge. It is generally been considered a haven and has thus been the go-to currency for investors during periods of economic turmoil and market distress. Additionally, gold can be used as a hedge against a decrease in the US dollar. As gold has historically been seen as a form of money, it acts as a good hedge against a USD collapse or hyperinflation.
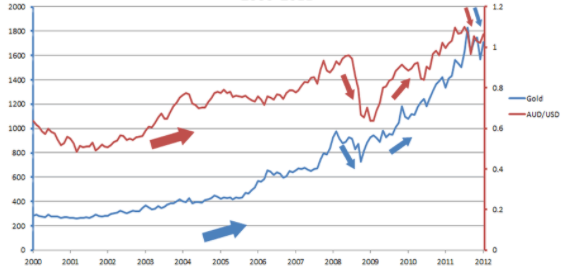
Hedging using forex correlation
As a novice, you will be surprised by the number of instances where currency pairs have correlations with each other. To apply this in practice, we have to implement what is known as “Pairs Trading”. The concept is pretty simple: you open a long position and a short position in two separate currency pairs. You can also substitute the second currency pair for a financial asset like oil or gold so long as a positive correlation between them exists.
You can implement pairs trading both in the long-term and short term. Market fluctuations do not affect your overall positions as it’s a market neutral strategy. It acts as a balancer of hedges against each other. This strategy can be used almost to perfection with some practice in volatile currency markets, as well as offer some much-needed diversity in your portfolio.
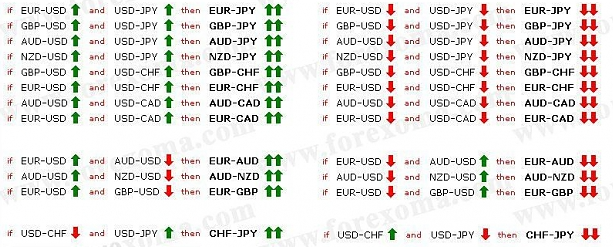
Swap hedging using cross currencies
Before discussing this strategy we have to first learn about cross-currency swaps, which are interest-rate derivate products. Two parties use separate currencies to exchange principal and interest rates. These are often international business or large scale investors. These currencies are not traded on a centralised exchange. This means that they can be customised at any point.
The two parties enacting cross-currency swaps do so to hedge the risk of inflated interest rates. They can even agree on a contract that imposes a fixed rate of interest to not incur losses if the market goes south. Cross-currency swaps are particularly useful for global corporations but you can also engage in them if you have a substantially large volume of FX to trade.
Options hedging in the FX market
Certain brokers offer instruments known as Forex options which are derivative products. It gives you the right but not the obligation to purchase or sell an FX pair at a specified price. It involves an expiration date after which the instrument expires. You can use FX options as short-term hedging strategies as they can expire at any moment. The options price is based on the market prices of the base currency of the currency pair.
For instance, if a trader opens a long position for AUD/NZD at 1.05, he looks for any sort of appreciation against the New Zealand Dollar. If it does at 1.07 for example, the trader can earn some nice payouts as a result. However, the trader should purchase a put option at 1.04 to limit losses. Even though options trading involves paying a premium to purchase them, it's still a cheaper alternative to other strategies. For example, if you accurately predict that AUD will increase in value you will get a handsome profit. If your prediction is incorrect, your losses would be limited to the premium.
Using Forward currency contracts
Forward currency contracts are similar financial derivatives where there is a contractual agreement between the buyer and seller to exchange foreign currency at a later date. There is more flexibility in this case as traders can settle the contracts on a cash or delivery basis at any point in time. You can also change the future expiration date, the currency pair traded or the volume of it involved. When it comes to hedging, this method entails much less risk.
Direct hedging
Direct hedging involves opening two directionally opposing positions on the same asset simultaneously. So if you have a long position already in a currency, short the same currency at the same time. The main reason why direct hedges are advantageous is that your trade remains on the market. You can close your direct hedge once the negative price movement is over.
Hedging using Oil
There are certain currencies that have a direct relationship with the oil price. For instance, the Canadian dollar has a positive relationship with the oil price as evident from its effect on the Canadian exchange rate. The USD/CAD weakens when the oil price strengthens and vice versa. So you can use the oil hedge strategy to hedge exposure on the USD/CAD trade. Alternatively, you open a long position USD/CAD and open a short hedge of the Oil.
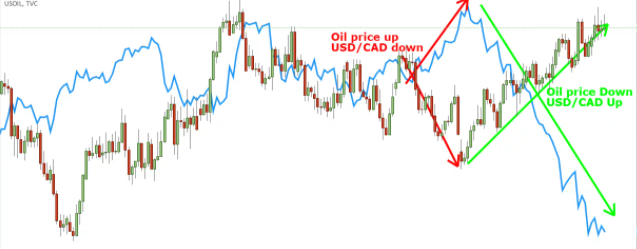
The risks involved with hedging for beginners
- It can get confusing: It can be somewhat overwhelming for forex traders to dive right into hedging especially if you're a beginner. So if you intend to use hedging as part of your wider risk management strategy, gain experience first. Demo accounts are a great way to do this as they simulate a real live forex trading environment.
- Limits potential profit: The more risk you take, the more profit you're likely to earn. So in this case, mitigating your risk will invariably limit your profit as well. So over-hedging should be avoided. The characteristic of a good trading strategy for FX offers protection from major losses in the short term but does not limit your potential for long term profit.
- Requires substantial capital: You would require quite a substantial amount of capital to effectively trade hedging strategies or be involved in hedge funds. This is difficult if you are a novice trader as they need to make sure he/she has sufficient funds to cover the risk. In case you are a small trader with limited capital, use minimal stop losses instead when attempting to grow funds.
Conclusion
Hedging is done not because it’s a good trading strategy but rather for psychological reasons. Financial hedging strategies especially in FX lets us know that we are not wrong about our trades but just holding it for a while. Thus, hedging can be likened to insurance against losses. It’s a helpful strategy to minimize risk on your fx trades, protecting against losses and helping build profits if you play your cards right.